EULAR2024 in VIENNAに参加しました(4)

みなさんこんにちは。
院長の伊達亮です。
先日開催された2024年6月12日(水)~2024年6月15日(土)にオーストリアのウィーンで開かれたヨーロッパのリウマチ学会(EULAR European League Against Rheu-matism)に参加してきました。
この学会は、アメリカリウマチ学会(ACR)と並んでリウマチ学では世界中でも最も規模の大きい学会の一つです。
スペインのA. Quevedo-Rodríguez医師のポスター講演を拝見しました。
リウマチ治療において頭を悩ませることの一つに、治療を変えても症状が改善しない患者さんがいることです。2020年EULARが定義した「治療困難なRA」(D2T RA)という言葉があります。今回の学会では、特にD2Tに関するまとまった報告が多く特に力を入れて聞いてみました。
POS0650
EVALUATION OF THE SURVIVAL AND SAFETY OF BIOLOGIC AND TARGETED SYNTHETIC DMARD IN PATIENTS WITH DIFFICULT-TO-TREAT RA USING DATA FROM THE BIOBADASER 3.0 REGISTRY
biobadaser 3.0レジストリのデータを用いた治療困難なRA患者における生物学的製剤および標的合成dmardの生存期間と安全性の評価
A. Quevedo-Rodríguez
Background:
- Biologic and targeted synthetic disease-modifying drugs (b/tsDMARDs) have changed the way rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is managed in recent years.
- Still, some patients remain symptomatic despite changes in treatment, which has led to the term “difficult-to-treat RA” (D2T AR), a definition proposed by the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR) in 2020 .
- To date, few studies have been published evaluating the drug survival and effectiveness of b/tsDMARDs in patients with D2T RA (2–4).
背景
- 生物学的製剤および標的合成疾患修飾薬(b/tsDMARDs)は、近年関節リウマチ(RA)の治療法を大きく変えてきた。
- 治療法を変えても症状が改善しない患者もいるため、2020年に欧州リウマチ学会連合(EULAR)が定義した「治療困難なRA」(D2T AR)という言葉が提唱された
- 現在までのところ、D2T RA患者におけるb/tsDMARDsの薬剤生存期間と有効性を評価した研究はほとんど発表されていない
Objectives: To compare safety and retention rate of b/tsDMARDs in those patients with a diagnosis of D2T RA included in the BIOBADASER 3.0 registry.
- D2T RAと診断された患者を対象に、b/tsDMARDsの安全性と投与継続率を比較すること
Methods:
- The EULAR definition of D2T AR was adapted according to the information available in the registry: patients who have received at least 2 b/tsDMARD with different mechanisms of action, that were discontinued due to ineffectiveness.
- The retention rate was analyzed using Kaplan-Meier curves considering the moment in which the patient meets D2T AR criteria as baseline.
- Regarding safety assessment, the incidence rate of adverse events was estimated.方法
- EULARのD2T ARの定義は、レジストリで入手可能な情報に従って適応された:作用機序の異なるb/tsDMARDを少なくとも2種類投与され、無効のため中止された患者。
- 維持率は、患者がD2T AR基準を満たした時点をベースラインとし、Kaplan-Meier曲線を用いて解析した。 安全性評価に関しては、有害事象の発生率を推定した。
- A total of 279 patients with a diagnosis of RA who met the adapted definition of D2T RA were included.
- Among the incorporated patients: 67, 66, 22, 89 and 35 were classified in the TNF inhibitor (TNFi), interleukin-6 receptor inhibitor (IL-6Ri), anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (anti-CD20), Janus-kinase inhibitor (JAKi) and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte–associated antigen-4 immunoglobulin (CTLA4-Ig) group, respectively.
- Concomitant treatment with conventional DMARDs (cDMARDs) was more common in the anti-CD20 group; with methotrexate (MTX) being the most frequently used.
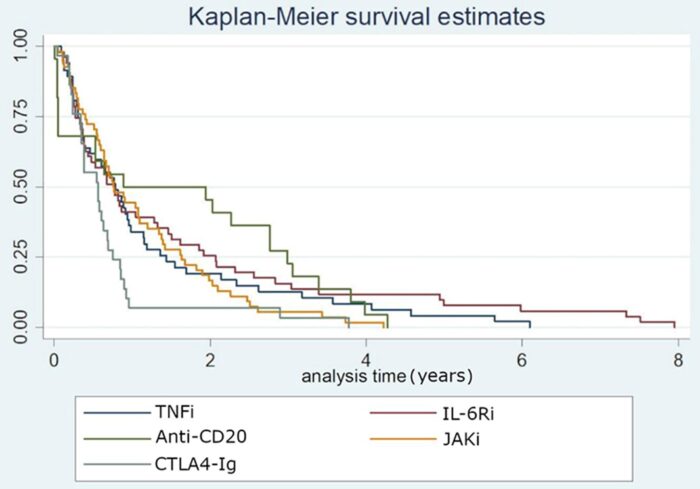
- Regarding drug retention, no statistically significant differences were detected except for the CTLA4-Ig group, which presented lower persistence (Figure 1).
結果
- 適応されたD2T RAの定義に合致するRAと診断された患者279例が組み入れられTNF阻害薬(TNFi)群67例、インターロイキン-6受容体阻害薬(IL-6Ri)群66例、抗CD20モノクローナル抗体(抗CD20 リツキシマブ)群22例、ヤヌスキナーゼ阻害薬(JAKi)群89例、細胞傷害性Tリンパ球関連抗原-4免疫グロブリン(CTLA4-Ig ABT )群35例であった。
- 従来のDMARDs(cDMARDs)の併用は抗CD20群で多く、メトトレキサート(MTX)の使用が最も多かった。
- 薬剤の持続性に関しては、CTLA4-Ig投与群で持続性が低かった以外は、統計学的に有意な差は認められなかった(図1)。
Results2
- In terms of safety, 312 AEs were recorded
- 61 serious AEs
- 4 fatal AEs
- The most frequent AEs were infections (n: 98; 31.4%)
- Patients in the CTLA4-Ig group showed the highest risk of Aes and serious Aes
- Fatal AEs occurred in the IL-6Ri (n: 3) and JAKi (n: 1) group.
結果 2
- 安全性に関しては、312件のAE(Adverse Event)が記録された
- 61件の重篤なAE
- 4件の致死的AE
- 最も頻度の高かったAEは感染症(n:98;31.4%)
- CTLA4-Ig群ではのリスクが最も高かった。
- IL-6Ri群(n: 3)とJAKi群(n: 1)では致死的AEが発生した。
Conclusion
- CTLA4-Ig presented lower drug retention rate and a higher AEs rate compared to the rest of the drugs in this D2T RA population, which could help guide therapeutic options in these patients.
- Further research is required in this regard to develop better recommendations.
結論 CTLA4-Igは、このD2T RA患者集団において、他の薬剤と比較して薬剤残存率が低く、AE発生率が高かった。 この点に関しては、より良い推奨事項を作成するためにさらなる研究が必要である。
実臨床でも感じていることですがABT製剤は若干2ndBio製剤としては、少し効果が薄い印象があります。AEsが多いことは、イメージと少し違っていました。
D2Tの患者さんには、早期寛解を目指して、JAK阻害薬を含めて、薬剤選択をしっかりと見極める必要があります。
文責 下関市 だて整形外科リハビリテーションクリニック 日本リウマチ学会専門医 伊達 亮

写真は、オーストリア国立図書館です。 18世紀に建てられたこの図書館ホールは、長さ80m、高さ20mあり、ドームはダニエル・グラン作の壮大なフレスコ画で装飾されています。 ここは世界で最も美しい歴史ある図書館の一つといわれているそうです。
文責 下関市 だて整形外科リハビリテーションクリニック 日本リウマチ学会 専門医 伊達亮
